
The Examination of Emerging Technologies for Their Potential Impact on and Use in Teaching, Learning, and Creative Inquiry in Schools: The NMC/CoSN Horizon Report: 2016 K-12 Edition – This is an eight-page summary of the 54-page report. In it, 55 experts weigh in what’s coming in the next five years. Use it to see how your school is doing.
Executive Summary
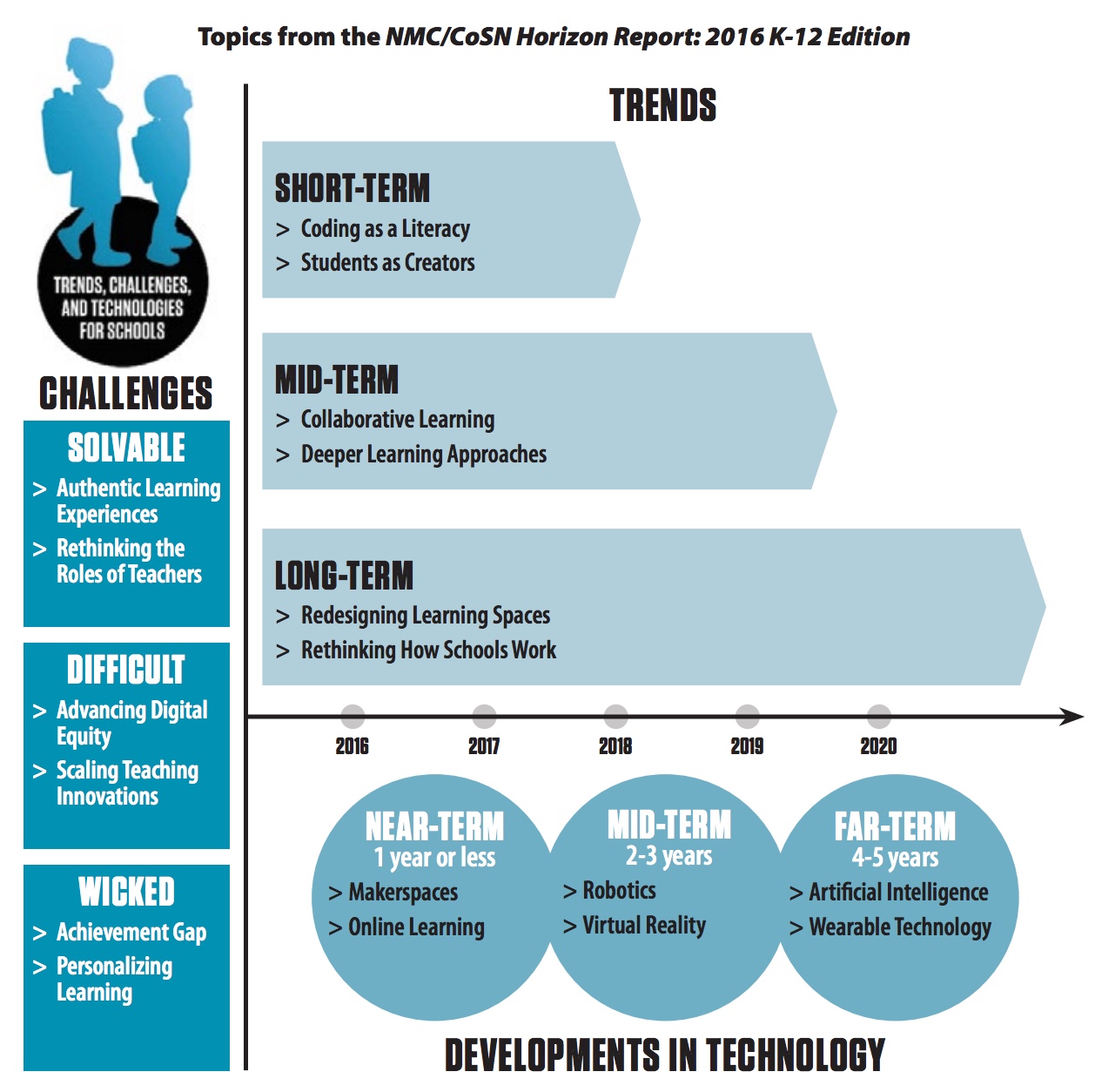
- The experts agreed on two long-term trends: redesigning learning spaces to accommodate more immersive, hands-on activities, as well as rethinking how schools work in order to keep pace with the demands of the 21st-century workforce and equip students with future-focused skills. In the short-term, the rise of coding as a literacy emerged as a new trend this year. There is a need for students to learn coding and programming skills, which have proven to bolster problem-solving, creativity, and critical thinking skills. K-12 leaders are already addressing the problem by partnering with local businesses to provide real-world experiences for students and expose them to different careers at a young age. When it comes to evolving expectations for teachers, both pre-service training and professional development are emphasizing creative technology use and scenarios where they transition from lecturers to guides and coaches.
- In the face of increasingly advanced technologies and quality learning materials, not every demographic has the same level of access, and learning outcomes are still unequal throughout the world. Online learning is expected to be widely adopted by schools in one year’s time or less to encourage students to take ownership of their education by creating and providing them with ubiquitous access to digital tools, discussion forums, rich media, and more. The time to adoption for robotics and virtual reality are estimated within two to three years, while artificial intelligence and wearable technology are expected to be mainstream in schools within four to five years.
Redesigning Learning Spaces
- While most classrooms employ a more than 100-year-old model with desks in rows and the teachers in front, there is an international move to change. More sunlight, healthier air, moveable furniture and walls, and student-centered pedagogy have all shown to improve performance. Self-lead student learning that is collaborative and social is replacing lecture-based instruction. A 1000-student school in Denmark features one large, open classroom with movable dividers. Like the remaining chapters, there are links for further reading that include: mobile technology transforming learning, creative learning spaces, green schools, innovative design, innovative learning spaces, and the rise of educational escape rooms featuring gameification of lessons.
Rethinking How Schools Work
- The overly regimented learning of traditional schools is being eclipsed by the recognition that formal education should mirror the way people learn and work in the 21st century. The latest crop of students is characterized as entrepreneurial, global thinkers who are highly social, visual, and technological. They are early adopters of digital tools, social media influencers, and aware of world issues. K-12 leaders are beginning to pilot competency-based models that certify the mastery of specific skills through students’ active demonstration of knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Teachers now post videos for students to watch at any time and there is an increased focus on solving real-world problems. Look to Finland and other Nordic countries where traditional subjects are being replaced by interdisciplinary classes. We also see more flexible options for students to redo assignments and retake tests. Self-guided learning is replacing classes altogether, which is very helpful for high-need students. Innovative campuses are starting to resemble a Silicon Valley workspace and there is a push to start school later.
Collaborative Learning
- Collaborative learning is becoming more pervasive in schools and classrooms throughout the world, with technology as a significant enabler. It is based on the principles of placing the learner at the center, emphasizing interaction, working in groups, and developing solutions to real problems. Educators also benefit through peer groups as they participate in professional development and interdisciplinary teaching. An added dimension to this trend is an increasing focus on global online collaboration. Successful collaborative learning strategies encourage increased student achievement, discussion, confidence, and active learning.
Deeper Learning Approaches
- Such approaches are defined as the mastery of content that engages students in critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration, and self-directed learning. Pedagogical approaches that shift the dynamic from passive to active learning allow students to develop ideas themselves from new information and take control of how they engage with a subject. These approaches include problem-based learning, project-based learning, challenge-based learning, and inquiry-based learning. The technologies leveraged to support deeper learning pedagogies are continually evolving and can boost the quality, breadth, and reach of student work and collaborative projects. It causes students to consider more than one side of a dilemma, use more comprehensive reasoning, and evaluate more frequently the importance of the assumptions underlying their decision-making. A number of organizations are providing support to schools to incorporate deeper learning.
Coding as a Literacy
- Many educators perceive coding as a way to stimulate computational thinking. The skills required to learn coding combine deep computer science knowledge with creativity and problem-solving. School leaders and technologists are making the case for embedding coding into K-12 curricula. Schools worldwide are developing coding programs in which students collaboratively design websites, develop educational games and apps, and design solutions to challenges by modeling and prototyping new products. Learning to code spurs the acquisition of 21st-century skills such as creativity and computational thinking, which can be applied to many jobs. A number of countries are starting to require all schools to teach coding and policy makers are trying to encourage more girls, blacks, and Hispanics to take coding. The job market is also a factor due to the abundance of computer science jobs.
Students as Creators
- Learners are exploring subject matter through the act of creation rather than the consumption of content. A vast array of digital tools is available to support this transformation. Many educators believe that honing these kinds of creative skills in learners can lead to deeply engaging learning experiences in which students become the authorities on subjects through investigation, storytelling, and production. This trend makes it essential that schools address the topic of fair use. Allowing teachers to make autonomous decisions is a defining characteristic of schools making progress here. Student-led lesson planning is a successful tool for promoting creativity and engagement, while bolstering student understanding of complex concepts. This also requires that the process of student assessment by revisited.
Significant Challenges Impeding Technology Adoption in K-12 Education
- Policy: The easiest to address is creating policies that spur the development of more authentic learning experiences. A more difficult area is creating policies that transition teachers into the 21st-century classroom role of guide and coach rather than lecturer.
- Leadership: Digital equity is a difficult task that leaders are just beginning to address effectively as not all learners have sufficient access to high-speed broadband internet at home to complete assignments. The most wicked leadership challenge is the achievement gap that persists, in which low-income students and other underserved learner populations struggle to stay in school and graduate with skills that translate to gainful employment.
- Practice: Categorized by the expert panel as difficult, the act of scaling teaching innovations requires school cultures that encourage education professionals to experiment with and collaborate on new approaches. Catering to each student by providing customized learning activities and support requires careful implementation and has been identified as a wicked challenge.
Authentic Learning Experiences
- Authentic learning experiences, those that bring students in touch with real-world problems and work situations, are still not pervasive in schools. These approaches include vocational training, apprenticeships, and certain scientific inquiries. Metacognitive reflection and self-awareness are cornerstones. An increasing number of schools have begun bridging the gap between academic knowledge and concrete applications by establishing relationships with the broader community. Through active partnerships with local organizations, learners can experience the future that awaits them outside of school.
- Five major obstacles to incorporating real-world learning in schools are: curriculum and content standards being too rigid; testing and accountability driving pedagogical decisions; schedules being too regimented and silos too restricting; educator practice requiring more risk-taking; and policy fostering a culture of achievement instead of teaching and learning.
Rethinking the Roles of Teachers
- Teachers’ primary responsibilities are shifting from providing expert-level knowledge to constructing learning environments that help students gain 21st-century skills including creative inquiry and digital literacy. Educators are now acting as guides and mentors, modeling responsible global citizenship and motivating students to adopt lifelong learning habits. Teachers are now tasked with changing their leadership style from directive to consultative and involving students in planning, implementation, and assessment. Evolving expectations are also changing the ways teachers engage in their own continuing professional development. Pre-service training needs to take all this into account and not gloss over digital learning strategies. Governmental policy makers have a big role here and most likely need prodding.
Advancing Digital Equity
- Pew Research reports that five million households in the US with school aged children are not privy to high-speed service. The growing pervasiveness of blended learning approaches is illuminating new gaps between those with and without high-speed broadband. Increased homework exacerbates this problem. Barriers to advancing digital equity are exacerbated as schools adopt flipped classroom approaches that rely on high-speed internet connectivity at home. Resourceful schools are overcoming these obstacles by providing students with greater flexibility and alternative places to do their homework. Some companies like Facebook and Google are working to expand access. Some schools are working with local providers to expand access and some have even equipped their buses with Wi-Fi.
Scaling Teaching Innovations
- Scaling pedagogical innovation requires adequate funding, capable leadership, strong evaluation practices, and the removal of restrictive policies. Scaling teaching innovations is an especially difficult challenge because variables such as teachers’ content preparation, students’ self-efficacy, and prior academic achievement vary across different contexts and significantly impact the effectiveness of educational interventions. Online learning, for example, has been a driver of many teaching innovations, but teachers frequently lack the time required to experiment and the institutional support needed to expand upon grassroots efforts. Optimal conditions in which innovation can proliferate include planning growth from the outset, understanding the operational realities of delivery, financing in a flexible and stable manner, and creating an enabling policy environment. Recognizing and assisting schools that have successfully scaled teaching innovations is a crucial part of addressing this challenge.
Achievement Gap
- Adaptive and personalized learning technologies are beginning to play a more integral role in identifying lower-performing students and student populations, helping educators and leaders understand contributing factors, and enabling and scaling targeted intervention methods and engagement strategies that help close the gap. Progressive systems that provide more funding to higher-need schools can help correct this imbalance. Investment in lower student-teacher ratios and higher teacher wages resulted in schools with smaller achievement gaps and better educational outcomes for low-SES students. Low-SES and minority students are statistically more likely to attend schools with inexperienced teachers and high staff turnover.
Personalized Learning
- The increasing focus on customizing instruction to meet students’ unique needs is driving the development of new technologies that provide more learner choice and allow for differentiated content delivery. Advances such as online learning environments and adaptive learning technologies make it possible to support students’ individual pathways. One major barrier is a lack of infrastructure in schools and poor homes. Personalized learning efforts must incorporate effective pedagogy and include teachers in the development process. Personalized learning can best be understood as an umbrella term for methods that enable students to achieve content mastery at an individualized pace. Textbook publishing companies are rebranding as learning management companies to offer smart products that play an active role in students’ learning.
Important Developments in Educational Technology for K-12 Education
- 1. Consumer technologies are tools created for recreational and professional purposes and were not designed, at least initially, for educational use — though they may serve well as learning aids and be quite adaptable for use in schools. These technologies find their ways into institutions because people are using them at home or in other settings.
- 2. Digital strategies are not so much technologies as they are ways of using devices and software to enrich teaching and learning, whether inside or outside of the classroom. Effective digital strategies can be used in both formal and informal learning. What makes them interesting is that they transcend conventional ideas to create something that feels new, meaningful, and 21st century.
- Enabling technologies are those technologies that have the potential to transform what we expect of our devices and tools. The link to learning in this category is less easy to make, but this group of technologies is where substantive technological innovation begins to be visible. Enabling technologies expand the reach of our tools, make them more capable and useful, and often easier to use as well.
- 4. Internet technologies include techniques and essential infrastructure that help to make the technologies underlying how we interact with the network.
- 5. Learning technologies include both tools and resources developed expressly for the education sector, as well as pathways of development that may include tools adapted from other purposes that are matched with strategies to make them useful for learning. These include technologies that are changing the landscape of learning, whether formal or informal, by making it more accessible and personalized.
- 6. Social media technologies could have been subsumed under the consumer technology category, but they have become so ever-present and so widely used in every part of society that they have been elevated to their own category. As well established as social media is, it continues to evolve at a rapid pace, with new ideas, tools, and developments coming online constantly.
- 7. Visualization technologies run the gamut from simple infographics to complex forms of visual data analysis. What they have in common is that they tap the brain’s inherent ability to rapidly process visual information, identify patterns, and sense order in complex situations. These technologies are a growing cluster of tools and processes for mining large data sets, exploring dynamic processes, and generally making the complex simple.
Makerspaces
- A growing number of classrooms, libraries, and community centers are being transformed into makerspaces, physical environments that offer tools and opportunities for hands-on learning and creation. Makerspaces are also increasing student exposure to STEM subjects and technical disciplines. Learners are applying maker skills to address some of the world’s pressing challenges with innovative solutions. Makerspaces are closely related to other educational trends such as collaborative learning, project-based learning, and student-directed learning. Student projects lead to new assessment techniques and student portfolios.
Online Learning
- Online learning has experienced a significant surge as more than 2.7 million students in the US alone are taking part. Educators are becoming more comfortable testing various levels of integration in their existing classes and programs, and many believe that online learning can be an effective catalyst for thoughtful discussion on all pedagogical practice. It has the potential to facilitate simulations that help students better understand and respond appropriately to real-life environments and situations. Indeed, major online learning trends include more project-based learning, personalized learning, and interactivity. Some attribute the acceleration of online learning to widespread 1:1 deployment and the impact of the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) movement. Hundreds of thousands of students are pursuing online-only education because of homeschooling, medical issues, or engagement in sports, while millions of other students are supplementing their in-class instruction with online courses to complete advanced coursework or gain greater schedule flexibility. When implemented effectively, online learning has the potential to help students graduate. Credit recovery, retaking courses to make up credits lost due to failing grades, is becoming a popular option in schools. More progress is needed to improve student success rates.
Robotics
- The global robot population is expected to double to four million by 2020 — a shift that will impact business models and economies worldwide. Robotics is two to three years away from mainstream adoption in K-12 education, potential uses are gaining traction for hands-on learning, particularly in STEM disciplines. Classes and outreach programs are incorporating robotics and programming to promote critical and computational thinking as well as problem-solving. Interaction with humanoid robots can help learners with spectrum disorders develop better communication and social skills. Robotics is a natural fit for makerspaces and other creation-centric environments where students are encouraged to invent and prototype. Governments around the world are devising STEM education strategies that prioritize the inclusion of robots and robotics activities. Like other areas, teacher training is vital here.
Virtual Reality
- While VR has compelling implications for learning, to date, it has been most prominently used for military training. Thanks to advances in graphics hardware, CAD software, and 3D displays, VR is becoming more mainstream, especially in video games. Virtual reality delivers immersive, simulated worlds, enabling complete focus on content without distractions. Students can engage in new situations and activities in realistic settings, fostering greater knowledge retention than textbook learning. Major investments are being made in prerecorded VR content for entertainment and sports, marketing, and education. In the K-12 sector, VR is well-positioned as an educational tool, generating immersive environments for field trips, with simulation and research activities serving as a prime enabler of student-centered, experiential, and collaborative learning. VR can overcome shortcomings in STEM education including a reliance on theory and lack of concrete experiences.
Artificial Intelligence
- As the underlying technologies continue to develop, AI has the potential to enhance online learning, adaptive learning software, and simulations in ways that more intuitively respond to and engage with students. The field was largely revived in 1997 after IBM’s advent of Deep Blue, the first computer to ever beat a chess grandmaster, and again in 2011 when IBM’s Watson defeated two Jeopardy champions. An overarching goal of this technology is to bolster productivity and engagement, better supporting the global workforce and individuals in their daily lives based on even the most subtle gestures. This makes AI promising for education, especially as teaching and learning increasingly take place online. The ability for people’s devices to better understand them and cater to their needs has been a major catalyst in advancing the field. Today, perhaps the most popular incarnations of AI have materialized in a growing host of virtual assistants, including Alexa, Cortana, and Siri. As students spend more time with the platform, the machine gets to know them better — just as a teacher or classmate would — allowing it to deliver more tailored content and recommendations over time. AI is at least five years away from widespread use in global K-12 education.
Wearable Technology – Time-to-Adoption Horizon: Four to Five Years
- Today’s wearables not only track where people go, what they do, and how much time they spend doing it, but now what their aspirations are and when those can be accomplished. This category also has potential to interest a variety of students in STEAM learning, as classroom activities can encompass multidisciplinary efforts of design, building, and programming. Recent consumer applications include devices that not only measure and record data, but also incorporate responsive assistance, helping individuals understand relationships between their bodies and surrounding environments. By integrating biometric information with other apps’ data, the device aims to help users identify stress triggers and balance physical and emotional needs. Wearable technologies help users adjust their behaviors to achieve goals. Schools are also introducing wearables into physical education.
DrDougGreen.com If you like the summary, buy the book





